How will Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation affect printers?
.png?width=750)
Laurel Brunner discusses the European Union’s Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation and how it is important for printers to be aware of this and it will contribute towards business planning.
What does the European Union’s (EU) Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation (ESPR) mean to you? Your likely answer will probably be, not a lot, but that could be a mistake even if your business is not based in the EU.
Much of the printing industry’s output is collateral work for goods and services. Brochures, leaflets directions for use, mini-catalogues and the like are bread and butter to the jobbing printer. Material can be printed using a range of printing methods and in run lengths from one to many thousands of copies. Print methods used range from digital and offset through to flexo and gravure according to the customer’s requirements. So far so sensible, but manufacturers of goods and providers of services to EU markets have some tricky new rules to follow. Print buyers all, these organisations are now required to comply with the EU’s ESPR; print service providers need to be aware of the regulation and how it impacts their customers. The regulation creates new requirements for communication and accountability, so the ESPR may create additional opportunities for printing companies.
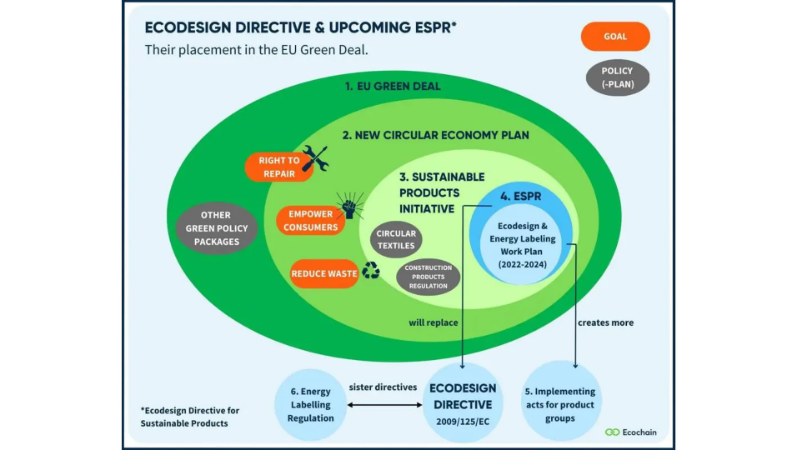
The goal with ESPR is to create a framework for sustainable products within the European Union. The regulation outlines the ecodesign requirements of different product groups, from cosmetics to toys, with the goal of making sustainable products the norm. ESPR sits at the heart of the EU’s Green Deal, a collection of policies which aims make the EU carbon neutral by 2050. The EU is spending over €1 trillion to implement this complex circular economy plan, including the Sustainable Products Initiative and the ESPR. This ambitious plan sets the global standard for circular economy initiatives.
According to the ESPR, a sustainable product will have certain characteristics compared to other products. For instance the product uses less energy in manufacture and in use, lasts longer and can be easily repaired. Compared to equivalents its parts can be easily disassembled and put to further use; the product includes fewer substances of concern, has a lower carbon and environmental footprint over its lifecycle, contains more recycled content and can be easily recycled.
Complying with the rules will be complicated to say the least, however goods and services providers will need to be able to demonstrate compliance. Printers can support their customers with this, but doing so will also be complicated. Identifying customers, including those who operate across geographies, who want communicate compliance to customers is probably the first step. Printers who can demonstrate awareness of the new regulation will have a competitive advantage over those who haven’t got a clue.
It will take a while for ESPR requirements to filter down to print service providers, but being aware in advance that it is coming will be an aid to business planning. And nine tenths of anything is preparation.
Image credit for cover image: This image was created by Ecochain for their ESPR 2024 overview blog which can be found here.
Recent news

Kodak's 2024 Sustainability Report: A Commitment to a Greener Future
Kodak's 2024 Sustainability Report, "One World, One Kodak," demonstrates a strong commitment to environmental and social responsibility. The report highlights impressive reductions in greenhouse gas emissions (56%) and water withdrawal (31%) and aims for zero waste by 2025. Notably, Kodak is pioneering double materiality assessment in the printing industry, aligning sustainability with financial reporting, and showcasing its products' environmental benefits.

How can printers lower costs on energy usage?
Clare Taylor outlines simple steps for businesses to achieve energy sustainability, focusing on cost savings and staff comfort. It emphasises starting with measuring energy consumption to identify key areas for improvement. Subsequent steps involve managing energy use through behavioral changes and low-cost interventions, like optimizing cooling settings and ensuring equipment is switched off when not needed.
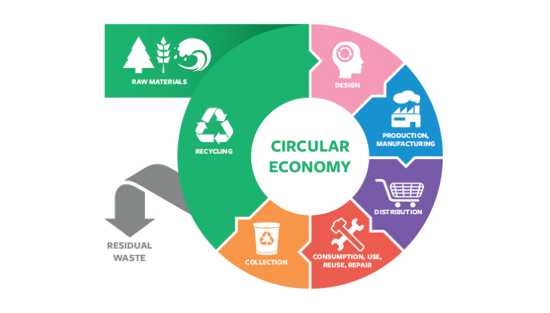
The European Union's circular economy plan
Printing companies must understand the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan (CEAP), part of the European Green Deal. These initiatives drive sustainability, impacting businesses globally, even if not EU-based, through customer requirements. Printers need to be aware of reporting and sustainability expectations to manage risks and retain clients.
A revised look at sustainability in wide format print
Sustainability is crucial for wide-format print, moving beyond marketing to an imperative driven by brands and regulations. Common "eco" claims often mask complexities; true sustainability demands carbon reduction as a core principle. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) offers data-driven insights for genuine environmental improvement, as demonstrated by UFABRIK's transparent approach.