
From 8th – 9th September 2022, the first edition of Textile Printing & Sustainability (TPS) conference took place in Dusseldorf. Participants came from all areas of the textile value chain and came from companies such as Avery Dennison, Fujifilm, Agfa, Epson, Marabu and FESPA. 120 participants from 15 countries attended.
From 8th – 9th September 2022, the first edition of Textile Printing & Sustainability (TPS) conference took place in Dusseldorf. Participants came from all areas of the textile value chain and came from companies such as Avery Dennison, Fujifilm, Agfa, Epson, Marabu and FESPA. 120 participants from 15 countries attended. The conference focused on all critical factors and global trends that currently influence the textile market look to the future. The conference featured experts from both screen and inkjet printing and included 25 presentations which focused on best practices, new application fields, automation, and sustainable business models as well as the benefits and challenges of each technology choice. These encouraged long discussions in the accompanying exhibition area where technology suppliers met with technology users, including printers and brands.
The conference was curated by ESMA, the European Association of Screen Printing Equipment Manufacturers. “Textile industry is more than ever under pressure from sustainability requirements”, explains Peter Buttiens from ESMA. The EU’s Green Deal targets textiles as one of the world’s most polluting sectors. On global scale, we look at UN Sustainable Development Goals and initiatives such as UN Alliance for Sustainable Fashion. Their timeline set for 2030 and 2050 may seem far in future but the time to act and exchange know-how is now. With the new TPS conference we want to contribute to the solution from the printing perspective.”
Debbie McKeegan, from Texintel and FESPA’s Textile Ambassador who was a moderator commented: “The Textile industry faces an uphill journey to a sustainable future. Sustainability isn’t just about environmental change it’s also about transforming and repositioning the traditional, outdated business models of a global industry and its stakeholders. Both can only be achieved with a radical overhaul of the supply chain in tandem with the application of new technologies. Market shifts are fast and furious, and the textile industry must adapt. All of which delivers both challenge and opportunity to the print sector. The challenge is to restructure, re-equip to deploy efficient digital machinery and digital data. Transparency and traceability are paramount, we need to unlock the supply chain to reveal the truth of all components. This is a once in a lifetime opportunity and one that will consolidate the industry to deliver sustainable production and efficient, environmentally secure manufacturing worldwide.”
In this article, we will look at the presentations that took place on day 1 of the conference including the takeaways from each presentation.
The key trends that were discussed on Day 1 were:
- investors and producers must rethink and revise their internal processes and consumers must be willing to pay more money for sustainable clothing.
- the need to have successful, sustainable leaders across all businesses
- compared to analogue printing, digital printing significantly reduces the consumption of water by approximately 60%, and reduces carbon emissions up to 95%, energy by up to 55%, whilst reducing waste potential by up to 85%.
- The future of textile will be digital textile printing and analogue printing methods will decline over time, on demand will be the new normal regardless of volume which has to be environmentally secure.
- The global textile market size was projected at $1 Trillion in 2020 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% from 2021 to 2028. The Global Digital Textile Printing Machinery Market is estimated to reach $2.25 Billion By 2028.
- Pigment inks are a sustainable ink solution seeing as they are a waterless technology
- Functional inks offer a new way in finishing and functionalisation of textile materials using screen printing and are emerging across digital technology.
- There is an increased need for white TiO2 pigments in DTG and DTF applications
Day 1
KEYNOTE: STEP UP TO SUSTAINABLE LEADERSHIP | Karin Ekberg from Leadership & Sustainability

Image Credit: TPS Conference
- Leadership engagement and communication
- Sustainability strategy as an integral part of the business strategy
- Integration into business processes and value chain approach
- Lean operations
- Business case
HOW CAN HARDWARE MANUFACTURERS MAKE A WORLD A BIT BETTER | Folker Stachetzki from Brother

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Folker Stachetzki, manages the marketing at Brother Industrial EMEA and is responsible for the CSR activities of the company and works closely with the sustainability departments responsible for Europe and Japan. Folker described how the industry is changing and emphasizes the need for investors and producers to rethink and revise their internal processes and for consumers to be willing to pay more money for sustainable clothing. Brother continue to launch several programmes to effectively implement sustainability goals and strive to make their products more sustainable. The 3 goals from Brother are to reduce CO2e emissions, resource circulation and biodiversity conservation which will be realised by 2050. Folker discussed the current sustainability opportunities through DTG printing which include producing printed shirts resulting in shorter delivery routes and a reduction of CO2e emissions, producing garments on demand resulting in less textiles being destroyed afterwards and using sustainable inks. He also shared how customers and producers are interested in automation, reduced waste and maintenance parts, MRSL requirements by big fashion brands and the certification of used chemicals and machinery.
TECHNOLOGICAL ADVANCES DRIVING INDUSTRIAL INKJET PRINT QUALITY IMPROVEMENT FOR TEXTILES | Tracey Brown from Meteor Inkjet

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Tracey, originally from the US spent her first 15 years of her career working with HP in management, marketing, and engineering. Tracey is the VP of Strategy and Marketing at Meteor Inkjet. Tracey emphasized the importance of using inkjet printing for textiles and focused on the environmental benefits. According to Xaar 2020 Annual Report, using inkjet printing reduces energy consumption up to 55%, water consumption up to 60% and carbon emissions by up to 95%. However, there are challenges with inkjet printing which include high costs, slow productivity from scanning machines due to the inefficiency of using multiple passes to hide errors and poor saleability of some single pass machines due to print quality and colour matching issues. Tracey emphasized the importance for businesses to have a simplified print system that starts with the PDF, then the RIP and then into a printing engine that focuses on nozzle compensation, stich adjustment, colour balance, screening, and calibration and from there moves onto printheads.
OPPORTUNITIES FOR PIGMENT INKS IN THE DEMANDING DIGITAL TEXTILE MARKET AND TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS | Rachel Li from Fujifilm Ink Solutions

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Rachel Li has over 17 years experience in inkjet printing and is currently the Segment Marketing Manager for Textile, Sign & Display, and Industrial in Fujifilm’s Ink Solutions Group. Rachel shared the key elements that drive digital textile which include sustainability, supply chains and extensive applications and how using the right ink technology can enable sustainable digital textile printing. Comparing analogue printing to digital printing, digital printing significantly reduces the consumption of water by 60%, and reduces carbon emissions by 95%, energy by 55%, and waste by 85%. Using digital and pigment textiles offer a sustainable solution for businesses, although some properties of digital printing may not be compatible with analogue printing. The 3 challenges in pigment formulation are colour, softness and fastness and productivity and jetting. It is important to take notice of small components as they contribute to the overall performance. These include pigment dispersion, co-solvents, binder, and additives.
ROLE OF ADDITIVES IN OPTIMISATION OF INKJET INKS FOR PRINTING OF TEXTILES | Dr. Vedran Durasevic from Evonik

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Dr. Vedran Durasevic runs the Inkjet and Decorative Inks Department at Evonik Coating Additives. In 2019, he researched the role of additives in the optimisation of inkjet inks for printing of textiles. In the presentation Dr. Vedran shared case studies that demonstrated how a selection of a wetting agent, and the pre-treatment of the substrate influence the kinetics of droplet spreading behaviour will be presented. Evonik’s laboratories are equipped with ImageXpert drop watcher and custom-made print stations which enables the visualisation of the spreading behaviour of droplets soon after being fired from industrial printheads. This allows the coverage ratio of the substrate by the ink to be quantified with respect to time, which gives way to determining differences between ink systems formulated with chemically different substrate wetting agents.
FROM VISION TO REALITY: BRIDGING GAPS IN DIGITAL TEXTILE PRINTING | Helmuth Haas from CHT Germany

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Helmuth is the project leader for digital printing at CHT, a worldwide chemical company with over 60 years of experience in textile auxiliaries and dyes. In his presentation, Helmuth discussed the importance of ink types and their effect on sustainability. The reasons for using digital printing with pigments can vary between early adopters and pragmatists, production is more efficient, there is a low MOQ (minimum order quantity) and a fast time to market. There are various sustainability models that include Pillar Model, Nested Model and Integrated Model.
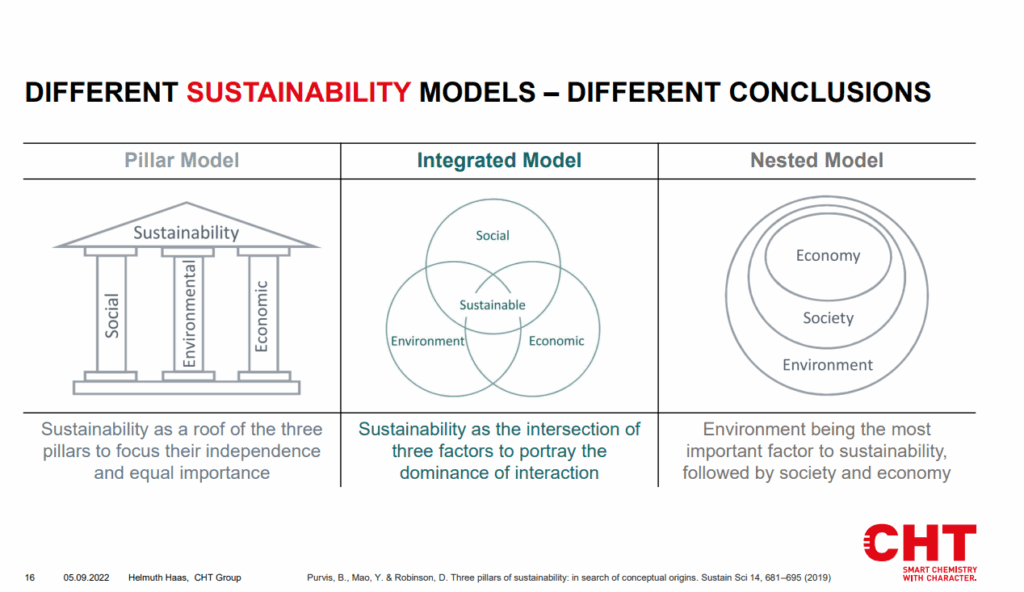
Image credit: presentation for TPS 2022 from Helmuth Haas from CHT Germany
Depending on the model, sustainability may be (more or less) the driver of change to digital technology, for example this could be due to the economic or environmental benefits. Despite consuming less energy, pigment in digital printing is not yet a dominant technology. Reactive and inks for cellulosics and dye sub and direct disperse inks for polyester are dominant and will stay the main inks in the future.
KEYNOTE: KEY MARKET SHIFTS AND INNOVATIONS DRIVING CHANGE FOR INDUSTRIAL PRINTED TEXTILES AND MANUFACTURE | Debbie McKeegan, FESPA Textile Ambassador

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Debbie McKeegan has over 25 years experience of professional multi-disciplinary experience in design and textile manufacturing and is an award-winning British designer. She is also the Textile Ambassador for FESPA. Debbie described that in the last 10 years there have been various challenges and new opportunities within the textile industry. The global textile market size was projected at $1 Trillion in 2020 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% from 2021 to 2028. The global digital textile printing machinery market is estimated to reach $2.25 Billion By 2028 (according to Persistence Market Research July 2022). There is an increasing demand for apparel from the fashion industry and a continuous growth of e-commerce platforms. The rapid developments in digital printing along with the rising penetration in the textile industry is anticipated to drive the market growth. Factors that are forcing change include consistent changes in consumer behaviour, key trends and shifts in buying cycles and using digital printing as a more sustainable method. A technology to watch for the future is pigment ink as it is a waterless technology. Debbie predicts that the future of textile will be digital textile printing and analogue printing methods will decline over time, on demand will be the new normal regardless of volume which has to be environmentally secure.
TURNING A DINOSAUR TEXTILE INDUSTRY INTO A CLEANTECH INDUSTRY | Dr. Simon Kew from Alchemie Technology

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Dr. Simon Kew has over 17 years experience in new product and process innovation applied to chemistry-enabled products and is a Director at Alchemie Technology. Within the textile sector, the single worst contributor to climate change is dyeing and finishing. By 2050, it is predicted that carbon emissions from dyeing and finishing textiles will triple to over 2 gigatonnes of CO2 annually, making it one of the most polluting industries on the planet. 20% of global water pollution is from textile dyeing and finishing. Alchemie offers “Endeavour”, a waterless smart dyeing solution that drastically reduces carbon emissions by cutting water used in the dyeing process by 95%, eliminating post-dye washing from the dyeing process. “Novara”, a digital precision finishing solution uses digitally controlled nozzles to deliver precise high-value fabric enhancing finishes exactly where they are required while removing water, chemicals, and energy. In addition, increased energy costs combined with demands from brands and consumers to improve supply chain sustainability means the way textiles are dyed and finished needs to urgently change.
VIVIDYE: REMOVABLE TEXTILE PRINTS | Johanna Nissen Karlsson from Vividye

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Johanna is co-founder and CEO of Vividye. Vividye innovation is a removable textile print that enables the reuse of textiles and offers a solution for removing colours from textiles. It features a 2-piece system that includes both the print and the removal of the print. 15% – 20% of all garments have print which hinders reuse and recycling which is an significant concern regarding recycling the garment. Vividye works with Swedish screen printing companies. The print is removed by using unique removal formulation, the removal process works with t-shirts that feature colour, the detergent is repeatedly reused. The print is developed to be functional in the exciting infrastructure of textile printing machines. The system promotes consumers to reuse, and encourages consumers to change their behaviour to use textile garments to their fullest lifespan before recycling. The aim of Vividye is to re-define printing on textile to re-integrate used textiles in the value chain, to prolong the lifetime of clothes and provide opportunities for upcycling, whilst enabling efficient material recycling when the textile is reaching its end of life.
ACCELERATING THE SHIFT TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE PRINTING TECHNOLOGIES ACROSS TEXTILE MARKETS: POLYURETHANES AS AN ENABLING MATERIAL SOLUTION | Dr. Inga Bargende from Covestro

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Dr. Inga Bargende is an industrial engineer and leads the business development and lab for digital textile printing as part of the Global Textile Coatings Team at Covestro. Dr. Bargende described that in order for the textile industry to become more sustainable, innovation is required. Digital Textile Printing featuring pigment inks have gained considerable attention and there is a need to move from analogue printing to digital printing. However, this technology requires advanced material solutions, Dr. Bargende has suggested that an appropriate material for printed textiles would be polyurethane raw materials due to their high flexibility, soft feel and excellent light fastness. Using this material offers excellent colour intensity, pleasant haptics and is suitable as pre-treatment and is a binder for pigment inks. Digital textile printing with pigment inks is predicted to reduce overproduction and accelerating the shift towards digital textile printing requires collaboration along the value chain.
NOVEL AQUEOUS WHITE PIGMENT CONCENTRATE FOR INKJET APPLICATIONS | Jürgen Bender and Dirk Imhof from Kronos

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Jurgen is Global Market Development Manager for Coatings, Inks and Paper at Kronos and Dirk has over 20 years of experinece in the industrial ink and coating market and is Head of Technical Service Department for inks and coatings at Kronos. Within textile and packaging applications there is an increased need for white TiO2 pigments particularly in DTG and DTF textile applications, printing white on KRONOS 9900 results in the highest opacity and whiteness on dark substrates. Trends across sustainability in this industry include the growth of digital packaging, pigment inks used for DTG and DTF white is necessary for vibrant colours and opacity and roll to roll printing will move from reactive dyes to pigments where possible. With governments across many countries pressuring the textile industry to reduce waste and water there is a need to ensure all businesses incorporate sustainability into their models.
SMART PRINTING FOR SMART PRODUCTS: USING CONDUCTIVE SCREEN PRINTING AND FUSED DEPOSITION MODELLING ON TEXTILES TO CREATE SMART TEXTILES | Katarina Windlands from RWTH Aachen

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Katarina is a research assistant at the Institute of Textile Technology at RWTH Aachen University. Additive manufacturing technologies allow for the creation of smart textile products by combining textile and non-textile components and thus extending the range of functions. By using conductive screen-printing technology with conductive pastes textiles with integrated electrical intelligent functions are created. Using this technology makes it possible to create unique and innovative human-machine interaction with solutions for monitoring, detection, lighting, heating, data exchange, etc. By using different material combinations based on fused deposition modelling, the development of textiles materials with unique hybrid features is possible. An example of this include 4D textiles that can change their form and function over time to adapt to their environment and the needs of their users. This change is generated by the complex interaction between hybrid materials and the use of external stimuli.
FUNCTIONALISATION OF TEXTILE SURFACES USING DIGITAL PRINTING TECHNOLOGIES | Dr. Reinhold Schneider from DITF Denkendorf

Image Credit: TPS Conference
Dr. Reinhold Schneider is Head of the research group Colour and Functional Printing at the German Institute for Textile and Fibre Research (DITF) in Denkendorf, Germany. Textile finishing improves the performance of textile substrates by implementing functions such as water repellence, UV-protection, flame-retardancy etc. in the textile substrate. Traditional printing uses high amounts of chemicals and is not flexible whilst digital printing technology only uses finishing chemicals on areas that are needed for the finished textile. Inkjet printing has significantly progressed and is a very fast and flexible application technology. With the development of functional inks this offers a new approach in finishing and the functionalisation of textile materials using digital printing technology.
A summary of all day 2 presentations and trends will be available shortly. FESPA’s Sustainability Spotlight feature at FESPA Global Print Expo 2023 will provide useful, informative and actionable advice to address the needs of People, Planet and Profit. Taking place from 23rd May – 26th May 2023 at Messe Munich, German. All conference sessions are free to attend that feature topics to provide the toolkit you need to reduce costs by optimising energy and resources. For more information on Sustainability Spotlight please visit here. If you would be interested in speaking at the feature please complete the enquiry form here.